Steve Jobs wasn’t accustomed to hearing “no.” But that was the answer from Paul Otellini, CEO of Intel.
It was 2006, and Intel, the global king of computer chips, was bringing in record revenue and profits by dominating the kinds of chips in hottest demand—for personal computers and data centers. Now Jobs wanted Intel to make a different type of chip for a product that didn’t even exist, which would be called the iPhone.
Otellini knew chips for phones and tablets were the next big thing, but Intel had to devote substantial capital and its best minds to the fabulously profitable business it already possessed. Besides, “no one knew what the iPhone would do,” he told The Atlantic seven years later, just before he stepped down as CEO. “There was a chip that they were interested in, that they wanted to pay a certain price for and not a nickel more, and that price was below our forecasted cost. I couldn’t see it.”
Otellini, who died in 2017, was a highly successful CEO by many measures. But if that decision had gone the other way, Intel might have become a chip titan of the post-PC era. Instead, it gave up on phone chips in 2016 after losing billions trying to become a significant player. As he left the company, Otellini seemed to grasp the magnitude of his decision: “The world would have been a lot different if we’d done it.”


Meantime, some 800 miles north, in Seattle, Microsoft was struggling to find its role in a tech world dominated by the internet, mobile devices, social media, and search. Investors were not impressed by its efforts. No one could have foreseen that years later, a few key decisions would set the company up as an AI powerhouse and send its stock soaring.
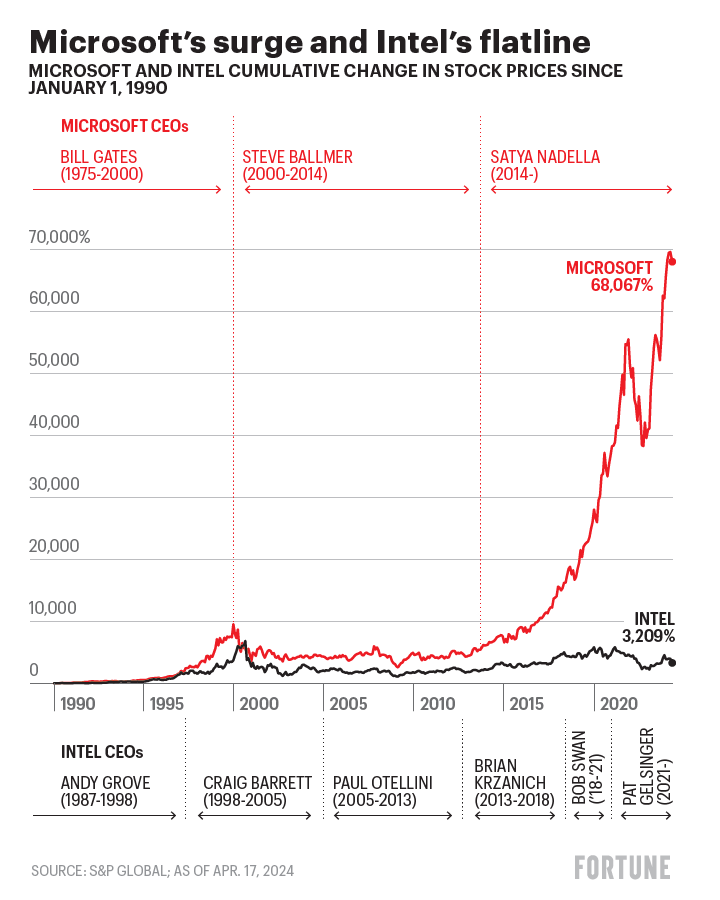
There was a time not so long ago that Microsoft and Intel were both atop the tech world. They were neither competitors nor significant customers of each other, but what New York University’s Adam Brandenburger and Yale’s Barry Nalebuff deemed “complementors.” Microsoft built its hugely profitable Windows operating system over the years to work on computers that used Intel’s chips, and Intel designed new chips to run Windows (hence “Wintel”). The system fueled the leading tech product of the 1990s, the personal computer. Microsoft’s Bill Gates became a celebrity wonk billionaire, and Intel CEO Andy Grove was Time’s 1997 Man of the Year.
Since then their paths have diverged sharply. Microsoft in 2000 was the world’s most valuable company, and after losing that distinction for many years, it’s No. 1 again. Intel was the world’s sixth most valuable company in 2000 and the largest maker of semiconductors; today it’s No. 69 by value and No. 2 in semiconductors by revenue, far behind No. 1 TSMC (and in some years also behind Samsung).

A Fortune 500 CEO makes thousands of decisions in a career, a few of which will turn out to be momentous. What’s easy to explain in hindsight—that Microsoft would be at the forefront of AI, that Google would become a behemoth, that Blockbuster would fade into obscurity—is never preordained. Often the fateful decisions are identifiable only in retrospect. Nothing more vividly illustrates this than the parallel stories of Microsoft and Intel. The case study of what went right and wrong at those two giant corporations offers a master class in business strategy not just for today’s front-runners at the likes of Google, Open AI, Amazon, and elsewhere—but also for any Fortune 500 leader hoping to survive and thrive in the coming decade.
Wintel’s origin story
The two companies were founded a mere seven years apart. Intel’s founders in 1968 included Robert Noyce, coinventor of the computer chip, and Gordon Moore, who had written the seminal article observing that the number of transistors on a chip doubled every year, which he later revised to two years—Moore’s law, as others later called it. Andy Grove was employee No. 3. All three are still regarded as giants of the industry.
Bill Gates famously dropped out of Harvard to cofound Microsoft with Paul Allen, a childhood friend. They were excited by the prospects of creating software for a new concept, the personal computer, also called a microcomputer. They launched Microsoft in 1975.


The two companies’ paths crossed when IBM decided in 1980 to produce a PC and wanted to move fast by using existing chips and an existing operating system developed by others. It chose Intel’s chips and Microsoft’s operating system, profoundly transforming both companies and the people who ran them. IBM’s size and prestige made its design the industry standard, so that virtually all PCs, regardless of manufacturer, used the same Intel chips and Microsoft operating system for decades thereafter. As PCs swept America and the world, Intel and Microsoft became symbols of technology triumphant, glamour, success, and the historic bull market of 1982 to 2000.
Then everything changed.
The reign of Gates and Grove peters out
In October, 2000, Fortune ran an article with an illustration depicting Gates and Grove as monumental Egyptian sphinxes. The headline: “Their Reign Is Over.”
The reasoning: “Gates and Grove attained hegemony by exploiting a couple of key choke points in computer architecture—the operating system and the PC microprocessor,” the article explained. “But in the new, more diverse IT world wired together by universal internet protocols, there are no such obvious choke points to commandeer.”
Thus began a multiyear identity crisis for both companies. Intel’s PC chips and Microsoft’s PC operating system and applications remained bountifully profitable businesses, but both companies and their investors knew those were not the future. So what was? And who would lead this new era?
In January of 2000, Gates stepped down as CEO after 25 years, and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft’s president and a college friend of Gates, took his place; Gates remained chairman. Two days later, Microsoft’s stock rocket ran out of fuel. On that day the company’s market value hit $619 billion, a level it would not reach again for almost 18 years.
Grove was no longer Intel’s CEO in 2000, having handed the job to Craig Barrett, a longtime company executive, in 1998. But as Intel’s visionary and most successful CEO, Grove remained an important presence as chairman of the board. His health was becoming an issue; he had been diagnosed with prostate cancer in 1995, and in 2000 he was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. Intel’s stock roared until August, when the company’s market value peaked at $500 billion. It has never reached that level since.
But most significantly, 2000 was the year that the internet began to seem like it just might make Wintel irrelevant.
At Intel, Barrett responded with acquisitions, many of which were in telecommunications and wireless technology. In concept, that made great sense. Cell phones were going mainstream, and they required new kinds of chips. “Craig tried to very aggressively diversify Intel by acquiring his way into new businesses,” says David Yoffie, a Harvard Business School professor who was on Intel’s board of directors at the time. “I would say that was not his skill set, and 100% of those acquisitions failed. We spent $12 billion, and the return was zero or negative.”
In the lean years after the dotcom balloon popped, Barrett continued to invest billions in new chip factories, known as fabs, and in new production technologies, so Intel would be well positioned when demand rebounded. That is a hint to one of the most important lessons of the Wintel saga and beyond: Protecting the incumbent business, even in a time of transition, is almost impossible to resist. That course usually sounds reasonable, but it holds the danger of starving the company’s future. As the great management writer Peter Drucker said: “If leaders are unable to slough off yesterday, to abandon yesterday, they simply will not be able to create tomorrow.”
‘We screwed it up’
At Microsoft in the 2000s, “it was not at all obvious what would happen with the shape and volume of PCs, with operating system margins, or the future of applications like Word or Excel,” says Ray Ozzie, a top-level Microsoft executive from 2005 to 2010. “There was significant internal debate at Microsoft and in the industry on whether, in the future, the PC was dead, or if it would continue to grow and thrive.” Maybe Word, Excel, and those other applications that resided on your hard drive would move to the internet, like Google Docs, introduced in early 2006. In that case Microsoft would need a new business model. Should it develop one? Some executives thought so. But no one knew for sure.
During this period, Microsoft was hardly a model of corporate innovation, and succumbed to what often happens when successful companies are disrupted. Ozzie explains: “When you are rolling in resources and there are multiple existential threats, the most natural action to protect the business is to create parallel efforts. It’s more difficult to make a hard opinionated choice and go all in. Unfortunately, by creating parallel efforts, you create silos and internal conflict, which can be dysfunctional.”
As competing teams fought for primacy, Microsoft missed the two most supremely profitable businesses since the PC era: search and cell phones. Those misses were not fatal because Microsoft still had two reliable, highly profitable businesses: the Windows operating system and the Office suite of apps. But in Drucker’s terms, those were yesterday businesses. Investors didn’t see substantial tomorrow businesses, which is why the stock price went essentially nowhere for years. Missing search and cell phones didn’t threaten Microsoft’s existence, but it threatened Microsoft’s relevance and importance in a changing world, which could eventually damage the company’s appeal among investors and the world’s best employees. The reasons for those crucial misses are instructive.
In 2000 Google was an insignificant internet search startup with no clear business model, but it had an inkling that selling advertising could be profitable. We know how that turned out: Google’s 2023 ad revenue was $238 billion. The model was entirely foreign to Microsoft, which made tons of money by creating software and selling it at high prices. Charging users nothing? Selling ads? Microsoft had never run a business at all like Google’s. By the time Google’s model had proved itself, Microsoft was hopelessly far behind. Today its Bing search engine has a 3% market share across all platforms worldwide, says the StatCounter web-traffic analysis firm. Google’s share is 92%.


Microsoft’s failure in cell phones was, in a large sense, similar—the company didn’t fully grasp the structure of the business until it was too late. The company assumed the cell phone industry would develop much like the PC industry, in which sellers like Dell combined Intel’s chips and Microsoft’s software in a final product. But Apple’s starkly different iPhone business model, in which it designs its own chips and writes its own software, was an enormous hit. The other big winner in the industry, Google’s Android smartphone operating system, likewise ignored the PC model. Instead of selling its operating system, Google gives it away to phone makers like Samsung and Motorola. Google makes money by putting its search engine on every phone and by charging app makers a fee when users buy apps.
Bill Gates acknowledges that Microsoft’s miss in cell phones was life-changing for the company. Looking back on his career in 2020, he said: “It’s the biggest mistake I made in terms of something that was clearly within our skill set.”
Intel also lost the mammoth cell phone opportunity, and in a similar way. It couldn’t adapt. Intel understood the opportunity and was supplying chips for the highly popular BlackBerry phone in the early 2000s. The trouble was, Intel hadn’t designed the chips. They were designed by Arm, a British firm that designs chips but doesn’t manufacture them. Arm had developed a chip architecture that used less power than other chips, a critical feature in a cell phone. Intel was manufacturing the chips and paying a royalty to Arm.

Understandably, Intel preferred to make phone chips with its own architecture, known as x86. Paul Otellini decided to stop making Arm chips and to create an x86 chip for cell phones—in retrospect, “a major strategic error,” says Yoffie. “The plan was that we would have a competitive product within a year, and we ended up not having a competitive product within a decade,” he recalls. “It wasn’t that we missed it. It was that we screwed it up.”
Groping for a megatrend
Just as 2000 was a turning point for Intel and Microsoft, so was 2013. Broadly they were in the same fix: still raking in money from the businesses that made them great; getting into the next big opportunities too late or unsuccessfully; groping for a megatrend they could dominate. Their stock prices had more or less flatlined for at least a decade. Then, in May 2013, Paul Otellini stepped down as Intel’s CEO. In August, Steve Ballmer announced he would step down as Microsoft’s CEO.
Succession is the board of directors’ No. 1 job, more important than all its other jobs combined. The stakes are always high. How the Intel and Microsoft boards handled their successions, nine months apart, largely explains why the two companies’ storylines have diverged so dramatically.
Under Otellini’s successor, Brian Krzanich, Intel kept missing new-chip deadlines—ironically failing to keep up with Moore’s law even as competitors did so—and lost market share. The company gave up on smartphone chips. After five years as CEO, Krzanich resigned abruptly when an investigation found he had had a consensual relationship with an employee. CFO Bob Swan stepped in as CEO, and the production troubles continued until, by 2021, for the first time in Intel’s existence, its chips were two generations behind competitors’. Those competitors were Taiwan’s TSMC and South Korea’s Samsung.
In crisis mode, Intel’s board brought back Pat Gelsinger, an engineer who had spent 30 years at Intel before leaving for 11 years to be a high-level executive at EMC and then CEO of VMware. As Intel’s CEO he has announced an extraordinarily ambitious and expensive plan to reclaim the company’s stature as the world leader in chip technology.
Microsoft’s board spent almost six months finding Ballmer’s successor under worldwide scrutiny. At least 17 candidates were publicly speculated upon. British and Las Vegas bookies offered odds on the eventual winner; Satya Nadella, who recently marked 10 years as CEO, was a 14-to-1 long shot.
Nadella has arguably been the best corporate succession choice, regardless of industry, in years or perhaps decades. Under his leadership the stock finally broke out of its 14-year trading range and shot upward, rising over 1,000%. Microsoft again became the world’s most valuable company, recently worth $3.1 trillion. Gelsinger, with just over three years in the job, can’t be fully evaluated; industry experts wonder if he’ll be Intel’s Nadella. But both CEOs offer useful examples of how to move a company from the past to the future.
Nadella orchestrated Microsoft’s dramatic turnaround by taking an outsider’s look at the company and making big changes with little drama. He began by making Office apps (Word, Excel) compatible with Apple iPhones and iPads—heresy at Microsoft, which regarded Apple as an archenemy. But Nadella realized the two companies competed very little, and why not let millions more people rely on Office apps? The move sent a message to the company and the world: The Microsoft culture’s endemic arrogance would be dialed down considerably. Interoperating with other companies could now be okay.
That was largely a new business model at the company, with many more to follow. For example, Nadella bought LinkedIn, a player in social media, which Microsoft had entirely missed, and later bought GitHub, a repository of open-source code, which Microsoft had previously despised. Both deals and several others have been standout successes.
More broadly, Nadella brought a new leadership style for a new environment. In a company known for vicious infighting that could paralyze action, he settled long-running debates over major projects. For example, in 2016 he sold the Nokia cell phone business that Microsoft had bought a year before he became CEO, acknowledging that the company had lost the battle for phones. “People don’t quite grok why things have blossomed under Satya,” says a former executive. “His superpower is to make a choice, eliminate conflict, and let the business blossom.”
At Intel, Gelsinger also introduced culture-defying changes. The company had risen to dominance by designing leading-edge chips and manufacturing them with industry-leading skill. Amid that intense pride, the idea of creating a separate foundry business—manufacturing chips designed by others—was anathema. Yet under Gelsinger, Intel has created a new foundry business while also relying more on other foundries, including TSMC, the world’s largest chipmaker, for some of its own chips—a double shock to the culture.
Getting a long-established company with a titanium-strength culture to adopt seemingly strange business models as Nadella and Gelsinger did can be painfully hard. Often only a new CEO can bring the openness necessary to make it happen. The same problem arises when a company needs to update its corporate strategy. Microsoft had been seeking and debating the next big thing for years, but Nadella saw that the company didn’t need to find a potentially huge new future-facing business. It already had one: Azure, its cloud computing service. Amazon Web Services was and is the industry leader, but Azure has grown to a strong No. 2 because Nadella has given it abundant capital and some of the company’s brightest workers. He also made an unorthodox investment in OpenAI, creator of ChatGPT, commiting $13 billion to the company starting before it was famous. Now Azure offers its customers OpenAI technology. In Drucker’s terms, it’s a big, thriving tomorrow business.
Gelsinger changed Intel’s strategy even more radically. He bet heavily and successfully on billions of dollars from the U.S. government. Via the CHIPS and Science Act, Intel could receive up to $44 billion in aid for new U.S. chip factories the company is building in coming years. “As I like to joke, no one has spent more shoe leather on the CHIPS Act than yours truly,” he tells Fortune. “I saw an awful lot of senators, House members, caucuses in the different states. It’s a lot to bring it across the line.”
A key insight is that for a major company with a history of success, like Microsoft and Intel, moving beyond an outmoded strategy and fully embracing a new one is traumatically difficult and sometimes impossible. For years both companies tried and failed to do it. A related insight: Doing it is easier for Nadella and Gelsinger because they have the advantage of being “insider outsiders,” leaders with deep knowledge of their organization but without heavy investment in its strategy; Nadella was working on Azure, not the Windows operating system or Office apps, long before he became CEO, and Gelsinger’s 11-year absence from Intel gave him license to rethink everything.
A larger lesson is that, in the stories of these two great companies, succession is the most important factor. Considering that Microsoft on the whole has fared better than Intel over the past 24 years, it’s significant that over that period, Microsoft has had only two CEOs and Intel has had five. Most people study the CEO when explaining a company’s performance, but they should first examine those who choose the CEO, the board of directors.
Looking back at these stories, asking “what if” is irresistible. What if Paul Otellini had said yes to Steve Jobs? What if any of Intel’s or Microsoft’s CEOs had been someone else? What if Intel, under a different CEO, had developed a successful GPU, the kind of chip that powers today’s AI engines (it tried)—would you ever have heard of Nvidia? Bill Gates said in 2019, “We missed being the dominant mobile operating system by a very tiny amount.” What if that tiny amount had shifted slightly? Whose phone would you be using today?
It’s all endlessly tantalizing but of course unknowable. The value of looking back and asking “what if,” is to remind us that every day leaders are creating the future—and neglecting their duty if they don’t learn from the past.
5 lessons from the Wintel case study:
1. Success can be a company’s worst enemy. The great management writer Peter Drucker said every company must “abandon yesterday” before it can “create tomorrow.” But in a successful company, every incentive pushes leaders to protect yesterday. Intel and Microsoft struggled for years to create their tomorrows.
2. Leaders must be open to business models that seem strange. Whether giving away software or manufacturing chips designed by others as a separate business, both Microsoft and Intel faced competitors doing things differently.
3. Get everyone on the same page. Debate is healthy up to a point, but at Microsoft it continued far too long until Nadella became CEO and set clear priorities. At Intel a series of CEOs backed differing solutions to its declining business, which prolonged a muddled strategy.
4. Succession is the board’s No. 1 job, more important than all its other jobs combined. Everyone knows it, but some boards still do their job poorly. If they make a mistake, none of the other lessons matter. Considering that Microsoft has come through the past 24 years better than Intel, it may be significant that Microsoft has had only two CEOs in that period while Intel has had five.
5. Failure isn’t fatal. The Wintel story is a pointed reminder that all companies, including the best, suffer failures and fall into crises. There are no exceptions. The leaders of any company, even the grandest, must always be ready to engage the skills of organizational rescue, and know that even that can be part of greatness.
This story was originally featured on Fortune.com

