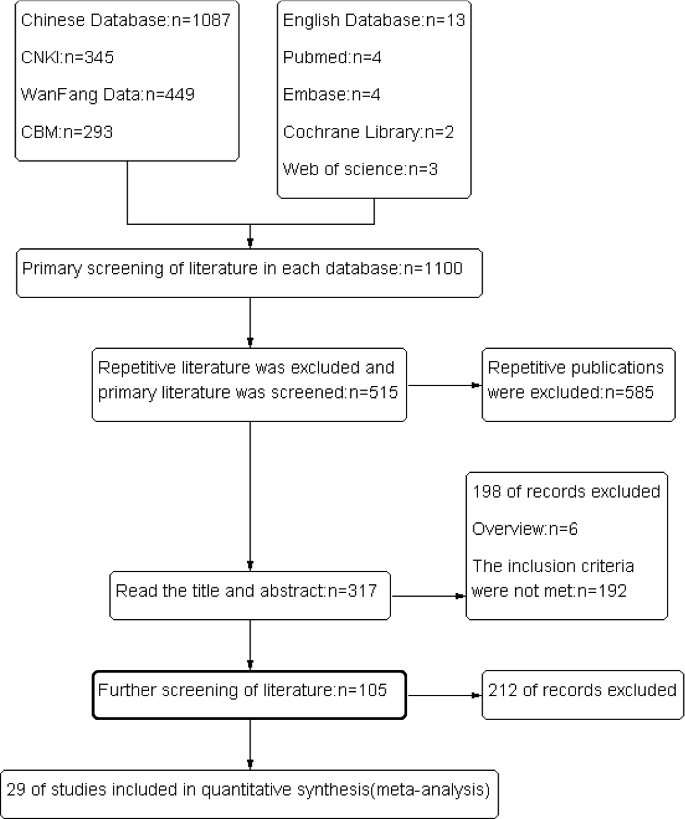
Literature search results
A total of 1,087 Chinese studies and 13 English studies were retrieved from the preliminary literature search. After screening titles and abstracts and excluding reviews and non-clinical studies, 317 articles were identified for full-text review, and 105 articles met our inclusion and exclusion criteria. Furthermore, through quality assessment screening, 29 of his RCTs were finally included in the meta-analysis, covering a total of 2903 of his TPE patients (1459 in the treatment group and 1444 in the control group in the UK). The literature screening process and search results are shown in Figure 3. Basic characteristics (Table 2) and bias risk assessment results (Table 3) are shown.
Drug efficacy analysis
Absorption time of pleural effusion
Eighteen RCTs were included in the analysis of pleural effusion absorption time. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between the included studies (x2 = 1581.44, i2 = 99%, P< 0.00001), a random effects model was used for the combined analysis.It was found that there was a statistically significant difference between the treatment and control groups [MD-5.82, 95%CI (−7.77, −3.87); P < 0.00001]This suggests that the treatment group was better than the control group in reducing the absorption time of pleural fluid (Figure 4).
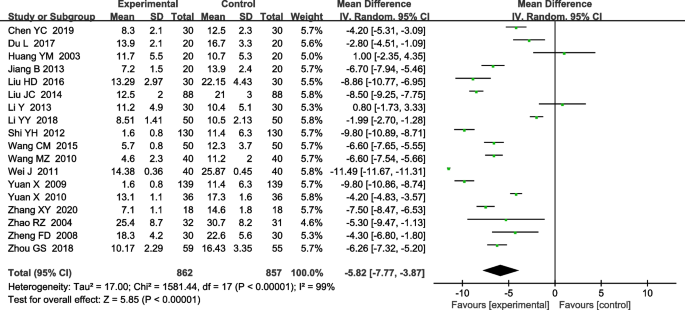
Meta-analysis forest plot of pleural fluid absorption time
Residual pleural thickness after treatment
A total of 16 RCTs reported UK effects on pleural thickness [4, 5, 11, 13,14,15, 17, 19, 22, 23, 27, 29, 30, 33, 35, 36]. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between the included studies (x2 = 1476.75, i2 = 99%, P< 0.00001)]a random-effects model was used for the combined analysis.It was found that there was a statistically significant difference between the treatment and control groups [MD-1.31, 95%CI (−1.70, −0.91); P<0.00001]This suggests that the treatment group was better than the control group in reducing pleural thickness (Fig. 5).
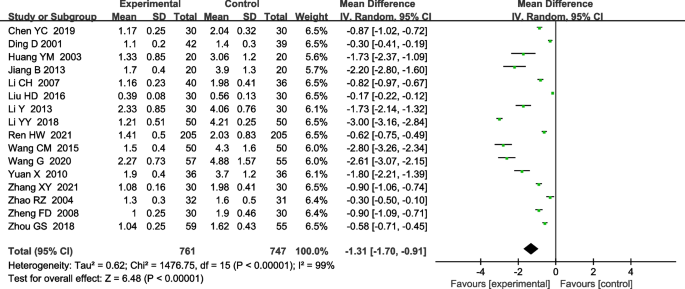
Meta-analysis forest plot of residual pleural thickness
Pleural fluid drainage volume
A total of 22 RCTs reported UK effects on pleural effusion output [4, 5, 10, 12,13,14,15,16,17, 20, 21, 23, 24, 26,27,28, 30,31,32, 34,35,36]. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between the included studies (x2 = 429.96, i2 = 95%, P< 0.00001), a random effects model was used for the combined analysis.Compared with the control group, pleural fluid drainage was clearly increased in the treatment group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD 822.81, 95%CI (666.46, 977.96); P<0.00001] (Figure 6).
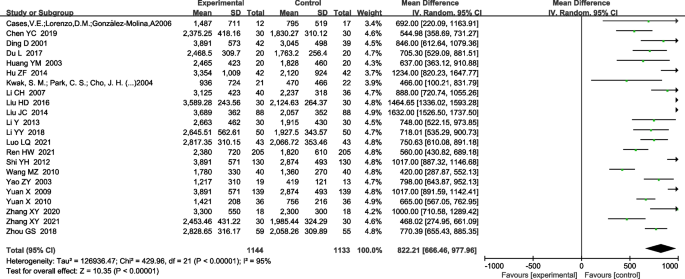
Forest plot of comparative meta-analysis of pleural effusion discharge
FVC% after treatment and FEV1% after treatment
A total of 4 RCTs reported UK effects on FVC% pred. [10, 15, 18, 34]. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between the included studies (x2 = 17.29, i2= 83%, P= 0.0006), therefore a random effects model was used for the combined analysis.It was found that there was a statistically significant difference between the treatment and control groups [MD 7.95, 95%CI (4.51, 11.40); P<0.00001], suggesting that the UK could have significantly improved. A total of 5 RCTs reported UK effects on FEV1%pred. [4, 10, 13, 15, 34]. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between the included studies (x2= 11.26, i2= 64%, P= 0.02), therefore a random effects model was used for the combined analysis.It was found that there was a statistically significant difference between the treatment and control groups [MD 12.67, 95%CI (10.09, 15.24); P<0.00001]suggesting that the UK was able to significantly improve lung function (Figure 7).
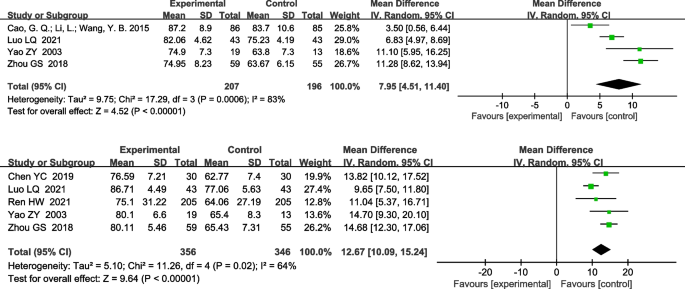
Forest plot of meta-analysis comparing FVC% pred and Forest plot of meta-analysis comparing Fev1% pred
Subgroup analysis
Subgroup analyzes were performed on UK doses among the 29 included RCTs.Specifically, there were two articles with UK doses less than 100,000 IU [16, 18] 22 articles with UK dose = 100,000 IU [4, 5, 11,12,13,14, 17, 19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28, 30, 32,33,34, 36]one article in UK dose = 125,000 IU [31]3 articles of UK dose = 200,000 IU [10, 15, 29]one article in UK dose = 250,000 IU [35].
UK FEV1% forecast
For the UK subgroup analysis on FEV1% pred, there were two papers where the UK dose was 200,000 IU. [10, 15]there are 3 articles with a UK dose of 100,000 IU. [5, 13, 34]. Both subgroups were analyzed using a random effects model. 200,000 IU subgroup differences [MD 12.14, 95%CI (7.21, 17.07); P < 0.0001] and in the 100,000 IU subgroup [MD 13.41, 95%CI (10.73, 16.10); P < 0.00001] Both were statistically significant (Figure 8).
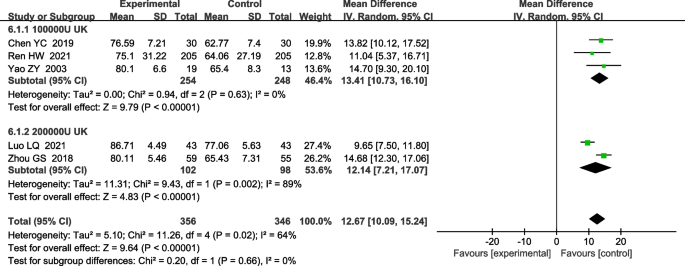
Forest plot for meta-analysis comparing Fev1% pred to controls in UK subgroups
UK on pleural thickness
For the UK subgroup analysis of pleural thickness, there were 13 articles with a UK dose of 100,000 IU. [4, 5, 11, 13, 14, 17, 22, 23, 27, 30, 32, 33, 36]2 articles for UK dose 200,000 IU [15, 29]. Both subgroups were analyzed using a random effects model.Similarly, the 200,000 IU subgroup difference [MD-0.73 (− 1.05, − 0.42), P < 0.0001] and in the 100,000 IU subgroup [MD-1.28 (− 1.76, − 0.80), P < 0.0001] Both were statistically significant (Figure 9).
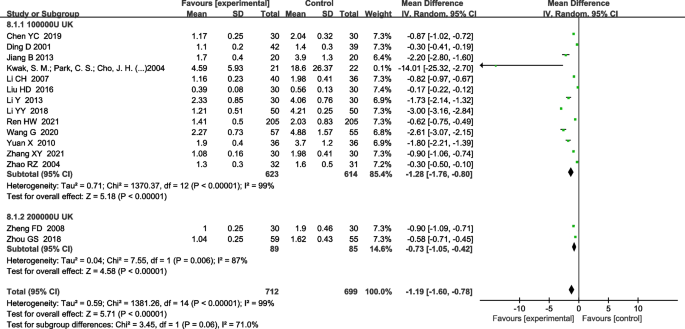
Effects of UK subgroup and control group on pleural thickness
UK regarding pleural effusion volume
For the UK subgroup analysis of pleural fluid output, there were 17 papers with a UK dose of 100,000 IU. [4, 5, 12,13,14, 17, 20, 21, 23, 24, 26,27,28, 30, 32, 34, 36]. Heterogeneity tests showed that heterogeneity existed between these studies (χ2= 413.68, P< 0.0001, i2= 96%). Therefore, when a random effects model was used in the combined analysis, the difference was found to be statistically significant. [MD 852.58 (658.051047.10), P < 0.0001]. In addition, he had two papers with a UK dose of 200,000 IU. [10, 15], including 102 subjects in the UK treatment group and 98 subjects in the control group. Heterogeneity tests showed that there was no heterogeneity between these two studies (χ2= 0.05, P= 0.83, i2= 0%).A random effects model was used for the combined analysis and the difference was also statistically significant. [MD 762.47 (673.48851.46), P < 0.0001] (Figure 10).

Effect of UK subgroup and control group on pleural effusion output
publication bias
A funnel plot was drawn with sample size on the vertical axis and effect size on the horizontal axis. Funnel plots of complete pleural effusion absorption time (Figure 11), residual pleural thickness (Figure 12), and pleural thickness (Figure 13) were all found to be asymmetric, indicating the presence of publications.bias [38]. Funnel plot analysis was not performed as subgroup analysis of FVC% pred and FVE1% pred included only a small number of studies.
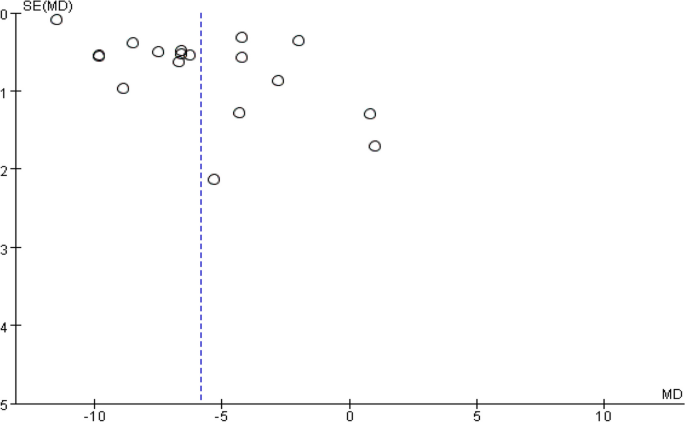
Time to complete absorption of pleural effusion, funnel plot
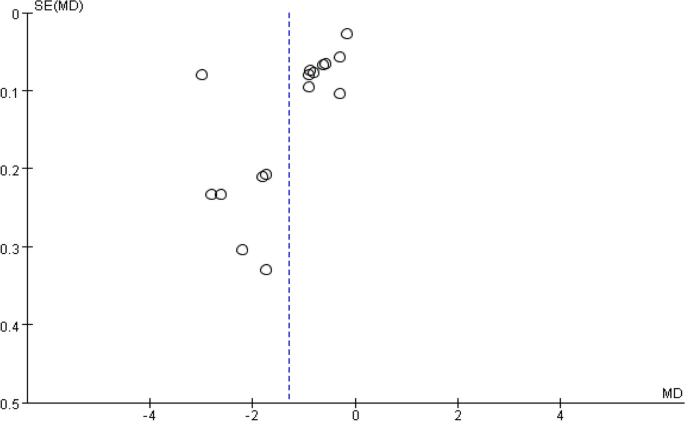
Residual pleural thickness, funnel plot
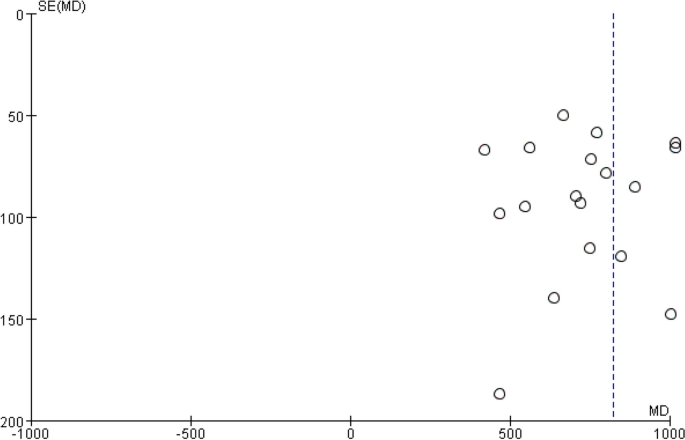
Pleural fluid drainage, funnel plot
